To know distribution of fundamental particles see Standard Model
A proton(H+) (not a fundamental particle) is a subatomic particle Conglomeration of three-quarks with two up quark and one down quark. Proton has a positive electric charge of 1.6*10-19C and a mass of 1.6726*10-27Kg. Its mass is 1836 times the mass of an electron. It combines with the neutron to give the atom most of the mass (Mass of an electron is negligible). The protons along with neutrons make the nucleus of atoms except for Hydrogen atom where the neutron is absent.
Rutherford confirmed the proton in 1920. In 2019, two different studies, using different techniques, have found the radius of the proton to be 0.833 fm (fermi). The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol Z). Each element has a unique number of protons and unique atomic number.
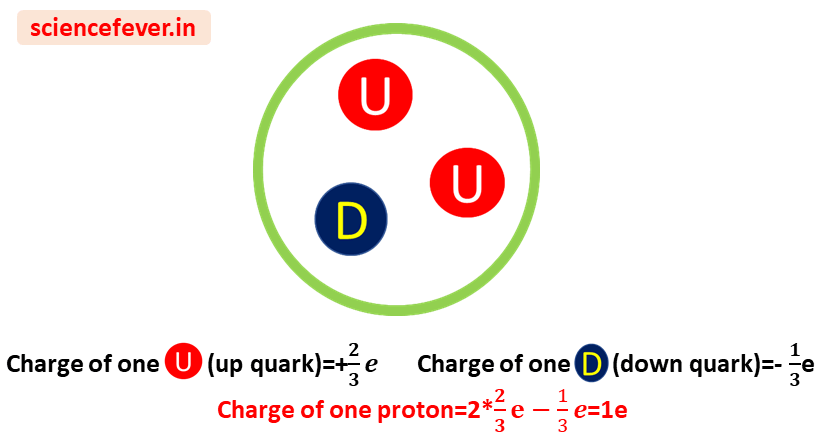
1. charge of proton:-
Earlier physicists considered proton as a fundamental particle. But in the modern Standard Model of particle physics,it is classified as a Baryon (like neutrons, ꓥ0, ∑+ ) which is under Hadrons. Three quarks combine to form a proton. Two up quarks of charge +2/3e and one down quark of charge –1/3e. So, its charge is 2/3e*2+(-1/3e) =+1e (i.e. 1.6*10-19C ).
2. mass of proton:-
The quarks inside the Proton move in the gluon field and interact with each other through gluon exchange. Inside the Proton during the gluon interaction anti-quarks also produced and disappeared. The mass of a proton is approximately 1.6726*10-27Kg. The rest masses of quarks contribute only about 1% of a proton’s mass. The remainder of a proton’s mass is due to the kinetic energy of the quarks. Gluon exchange also produces energy. So, this high energy contributes to the remaining mass of the Proton.
3. Discovery:-
- In 1815, William Prout proposed that all atoms are composed of hydrogen atoms (which he called “protyles”).
- In 1886, Eugen Goldstein discovered anode rays and showed that they were positively charged particles produced from gases.
- The nucleus was discovered In 1911 by Ernest Rutherford .
- Ernest Rutherford shot beams of alpha particles into the air and detected hydrogen nuclei with scintillation detectors.
- After investigating further, Rutherford found that the nitrogen atoms present in the atmosphere produced these hydrogen nuclei.
- He fired beams of alpha particles into pure nitrogen gas and observed that a greater number of hydrogen nuclei.
- In 1920 he proposed the name for the positive hydrogen nucleus as “Proton” as inspired by William Prout’s word “Protyle”.
- This experiment was the first to report a nuclear reaction and the equation was: 14N + α → 17O + p(proton)
- In 1917 Rutherford discovered that the hydrogen nucleus (known to be the lightest nucleus) could be extracted from the nuclei of nitrogen by atomic collisions.
- Thus he came to know that it is a fundamental particle. It is the building block of nitrogen and all other heavier atomic nuclei. Some consider it as the discovery of proton









This amazing article helped me to gather more knowledge as we were generally known about fundamental quantities of these systems…