The velocity of a body is defined as the rate of change of position w.r.t. a frame of reference /relative to another body. It is a vector quantity that defines how fast a body moves in a certain direction. If you consider two bodies moving in the same direction with different velocity then the body with higher velocity moves faster than the other. The body moving with higher velocity covers more distance in the same time than the other. As it is derived from two fundamental quantities it is called derived quantity.
| Symbol | |
| Unit | m/s, km/h |
| Dimensional formula | LT-1 |
| Vector/Scalar | Vector |
| Fundamental/Derived | Derived |
Though the S.I. unit of velocity is m/s but in practice we use km/h.
Table of Contents
Types of velocity:-
1.Average velocity:-
Average velocity is defined as the total displacement over total time.
Consider a body moves 30km towards the east and reaches B. it is obvious that he will not move with the same velocity throughout the road. Sometimes he will move faster on traffic-free roads and sometimes he will move slower on crowded roads . So it will be great to calculate average velocity instead of velocity.

Average velocity ,
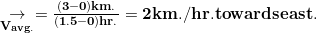
If we break his whole path into small segments, each with some time interval then
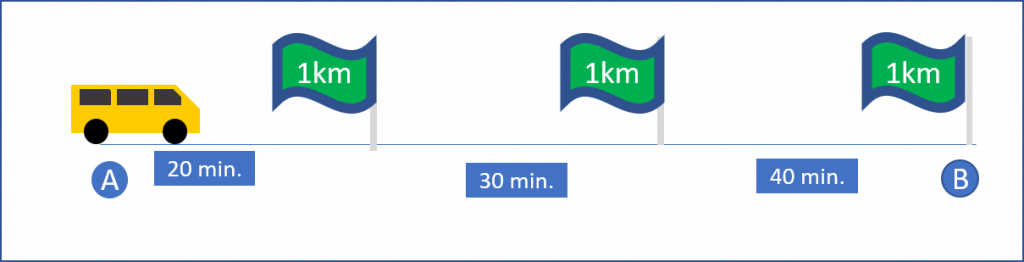
| Distance (km.) | Time (min.) |
| 1 | 20 |
| 1 | 30 |
| 1 | 40 |
Then his average velocity will be

2.Instantaneous velocity:-
Instantaneous velocity is defined as the velocity of a body at any instant. for example, you are driving a bike in a specific direction. At any instant suppose at 8 am you looked at your speedometer and it shows as 40km/hr. that means at 8 am your velocity was 40km/hr in that direction. To calculate the instantaneous velocity you have to record your speedometer at that instance.
Mathematical formula:-
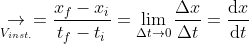
The above formula suggests that the velocity is said to be instantaneous when the time difference is so small that we can take the initial time and the final time as the same.
Difference between average velocity and instantaneous velocity:-
| Average velocity | Instantaneous velocity |
| (1) The average velocity of a body remains the same irrespective of the path. (2) The time difference is more. | (1) Instantaneous velocity of a body may be different at different instant. (2) The time difference is negligible. |
3.Initial velocity:-
It is the velocity possessed by the body at the beginning of the experiment.
For example a body started to move from left to right and crossed the point A. Here the initial velocity of the body is the velocity noted when the body reached the point A.
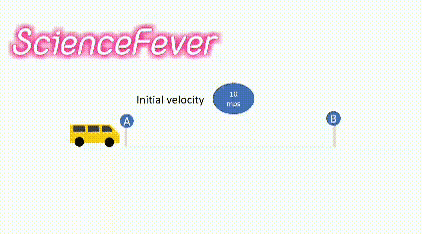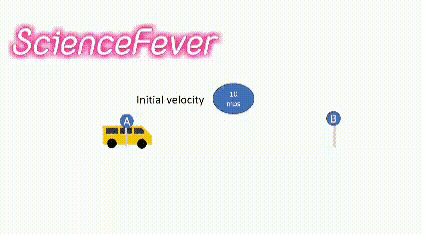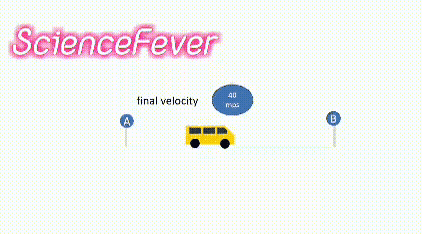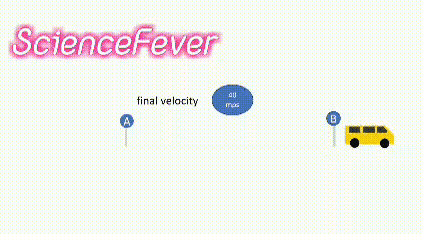
4.Final velocity:-
The final velocity is the velocity possessed by the body at the end of the experiment.
In the above example, the final velocity is the velocity possessed by the body when it reached the point B.
We can also calculate the final velocity by using the equation of motion.
For example, consider a body having an initial velocity of 10m/sec. with a acceleration of 2m/s2. Then what is the final velocity(![]() ) after 15sec?
) after 15sec?
![]() =10m/sec, t=15 sec. ,
=10m/sec, t=15 sec. , ![]() =2m/s2
=2m/s2
final velocity ,![]() =
=![]() +
+![]() t ,
t , ![]()
![]() =10+15*2=40 m/s2 with direction.
=10+15*2=40 m/s2 with direction.
5.Constant Velocity:-
A body is said to have constant velocity if it maintains the same speed in the same direction throughout the journey.
If a body moves with constant velocity then it simply means its initial velocity and final velocity are the same (i.e v=u).
v=u+at ![]() v=v+at
v=v+at![]() a=0
a=0
If a body moves with constant velocity(no change in speed and velocity) then it has no acceleration (a=0).
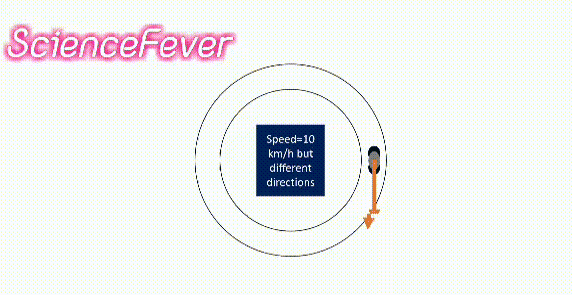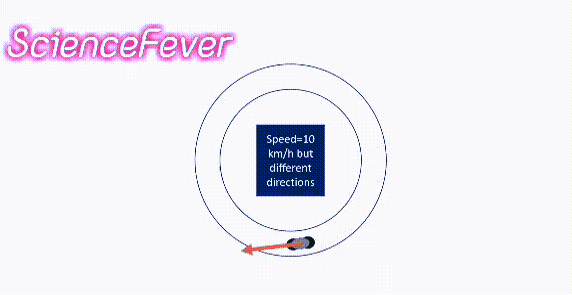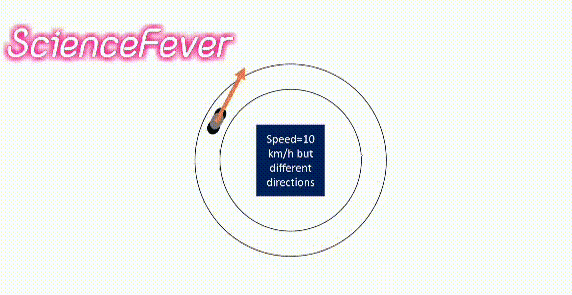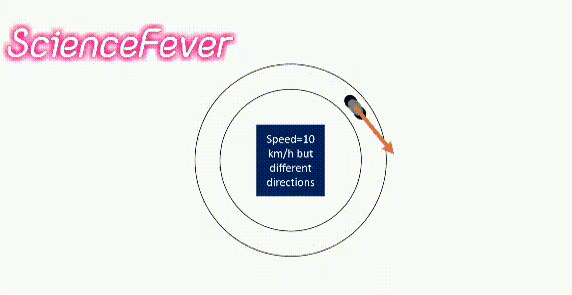
If the body changes its speed or direction(i.e change its velocity) or both then the velocity will change.
For example, a body moves with the same speed in a circular path. its velocity is not constant as it changes its direction continuously.
How to calculate the velocity ?
Consider a body moves 30km towards the east from O to B in 2hrs.
Then its velocity=30/2=15km/hr. towards east.
If the same body moves the same distance in same time towards the west from O to A.
Then its velocity =-30/2= -15km/hr. towards west (i.e opposite direction.)
Difference between speed and velocity :-
Velocity=speed + direction
That means the speed in a specific direction is called velocity. This also means that the magnitude of the velocity is called speed.
| velocity | speed |
| 1.Speed along with the direction is specified. 2.It is the displacement per unit time. 3.If a body returns to its initial position its velocity is 0. | 1.Only speed is considered. 2.It is distance covered per unit time. 3.If a body returns to its initial position it has some speed. |
Relative Velocity:-
Velocity of a body w.r.t. another is called relative velocity of that body.
(i) For example, consider a body A moving with velocity 50km/hr. another body B is moving with a velocity 30km/hr. Then the relative velocity of the body A w.r.t. B is
That means the body B moves slower than A.
Again,
(ii) If a body A moves with a velocity 20km/hr. w.r.t. a body at rest then the relative velocity of A w.r.t. B is V=20-0=20km/hr. with direction.
(iii) If two bodies A and B moves with velocities 30kmph and 40kmph in opposite direction then the relative velocity of A w.r.t. B is
![]() AB=30+40=70kmph
AB=30+40=70kmph
Other Velocity Terms: –
1.Orbital Velocity: –
The velocity required to revolve a satellite around the orbit of earth is called orbital velocity.
2.Escape Velocity: –
Escape velocity is the minimum velocity required for a body to escape from the earths surface.
3.Drift Velocity: –
Drift velocity is the average velocity possessed by the charge particle due to electric field.
Other quantities expressed by velocity: –
- Acceleration:-
It is the rate of change of velocity.
- Momentum:-
Momentum of a body is defined as the product of mass and velocity.
- Angular Velocity(ω): –
It is the ratio of linear velocity to the radius.
- Kinetic energy: –
It is the energy possessed by the body due to its motion.









I had doubt about relative velocity & this article has cleared all my doubts. I am eagerly waiting a new article on ‘Projectile Motion Considering Drag’.
Details expansion of velocity. You describe all about velocity and all type of velocity. Good job👍👍. Keep writing . Please write different fact of physics.