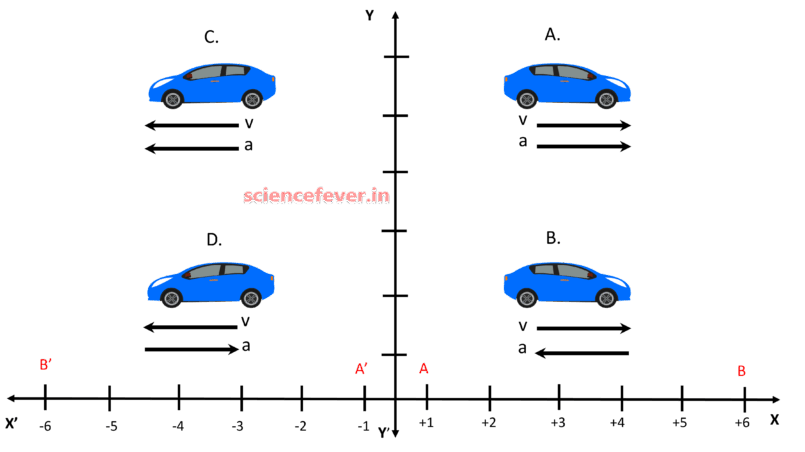
Retardation/deceleration is defined as the acceleration in the direction opposite to the direction of the velocity. Retardation and deceleration are same thing. Retardation/deceleration causes decrease in velocity. SymbolS.I...
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity of a body. It is a vector quantity and it defines how quickly a body changes its velocity. If we set a speed limit for two bodies, the body which has more acceleration...
The velocity of a body is defined as the rate of change of position w.r.t. a frame of reference /relative to another body. It is a vector quantity that defines how fast a body moves in a certain direction. If you consider two...
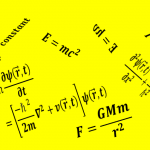
A wave function is a mathematical function which represents the matter-wave of a particle. It has no physical form like water waves, sound waves, or waves in springs. But we can represent or interpret it graphically. It contains...
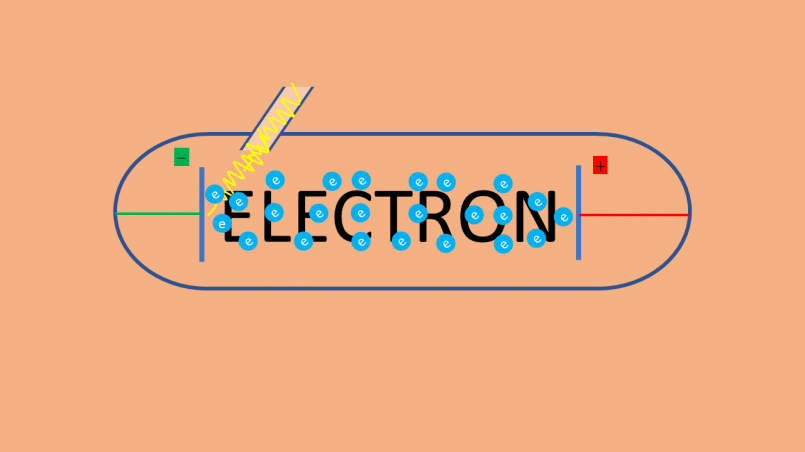
The electron is a fundamental particle having a mass of 9.11*10-31kg (energy equivalence of 0.511Mev) and a charge of 1.6*10-19c. It was discovered by J.J Thomson in 1897. In the standard model of physics, it is categorized as...
Projectile Motion is the motion of a body under the influence of gravity only. A body which moves with constant velocity in horizontal direction and experience uniform acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s2) in vertically downward...
Most people use the mailing service of google i.e. Gmail. Sometimes you may have send a wrong information to somebody or send to a wrong person. But what if you can undo that email before the receiver got it. Follow these steps...
A quantum computer uses quantum principles like superposition, entanglement & interference for computation. The quantum particles behave differently than our classical perception known as Quantum Weirdness. Superposition...
Meet the agile robot of future- ‘Spot’. Boston Dynamics has launched its quadruped robot “SPOT”. It is advanced than the wheel-based robots and walks like a tetrapod. This guy is flexible and can walk in rocky...
To know distribution of fundamental particles see Standard Model A proton(H+) (not a fundamental particle) is a subatomic particle Conglomeration of three-quarks with two up quark and one down quark. Proton has a positive...